Top 5 Cartoon Drawing Filter Apps of 2023 for Photo to Cartoon Conversion
5 Best Photo to Cartoon Drawing Conversion Filter App in 2023 If you are a fan of cartoons and want to turn your photos into fun and quirky cartoon …
Read Article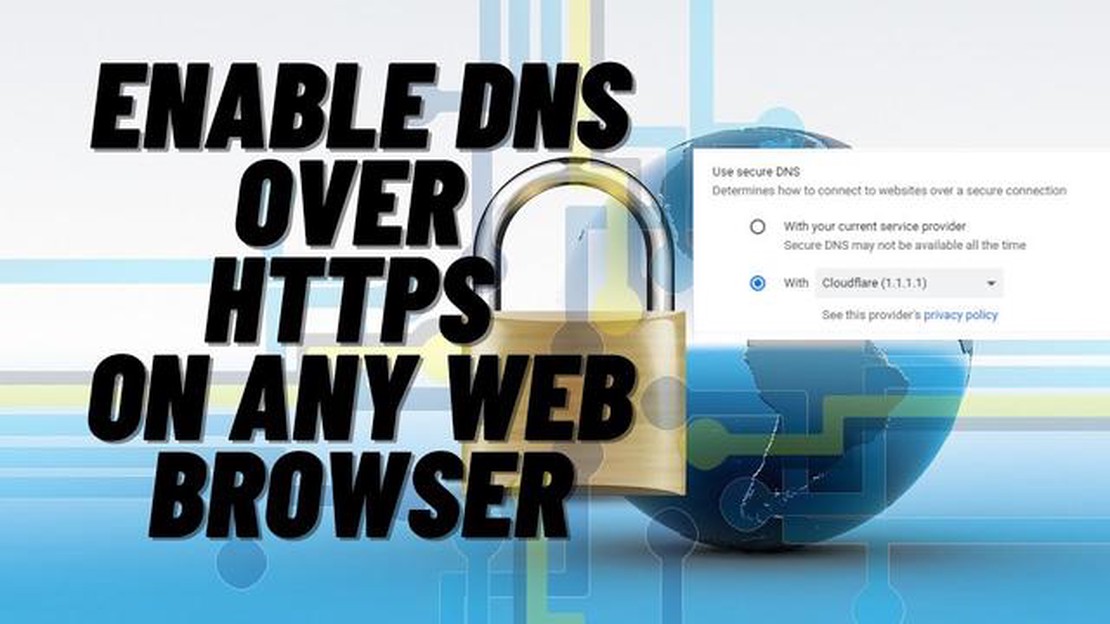
Protecting your privacy online is important, and one of the key aspects of that protection is securing your DNS traffic. To accomplish this, there is a protocol called DNS-over-HTTPS (DoH), which provides encrypted data transfer between your device and DNS servers. In this article, we will show you how to enable DNS-over-HTTPS in all popular Android browsers.
Enter your browser settings by tapping on the “Three Dots” icon in the top right corner of the screen. Then select “Settings” from the drop-down menu.
Scroll down to the “Security” section and click on “DNS connection method”. In the window that appears, select “DNS-over-HTTPS.”
Note: If you are having trouble connecting to the DNS server, you can select the “ask server about protocol” option.
Open the browser and enter its settings by clicking on the “Three Stripes” icon in the upper right corner of the screen. Then select “Add-ons” from the drop-down menu.
Under “Extensions,” find and install the “DNS-over-HTTPS” extension from Mozilla. After installing the extension, restart your browser.
Open your browser settings again and scroll down to the “Privacy and Security” section. In this section, find the “Use DNS-over-HTTPS” setting and turn it on.
Open settings in your browser by clicking on the “About” icon at the bottom of the screen. Then select “Settings” from the menu.
Under “Security and Privacy,” scroll down the page and find the “DNS-over-HTTPS” setting. Toggle it to the “Enabled” position.
Now that you have activated DNS-over-HTTPS in all your Android browsers, your DNS traffic will be protected and securely encrypted.
DNS-over-HTTPS (DoH) is a protocol that provides a secure and private connection to DNS servers. It encrypts DNS queries so that third parties can’t snoop on your online activities. In this article, we will look at how to enable DNS-over-HTTPS in different browsers on Android devices.
If you are using Microsoft Edge on an Android device, DNS-over-HTTPS support is automatically enabled with no option to disable.
Once DNS-over-HTTPS is activated in the selected browsers on your Android device, all DNS queries will be secure and private. This will provide a more secure and private internet connection.
DNS-over-HTTPS (DoH) is a protocol that provides encrypted transmission of DNS redistributor queries over HTTPS.
Activating DNS-over-HTTPS in all browsers brings the following benefits:
Overall, activating DNS-over-HTTPS in all browsers provides privacy, security, and reliability when using the Internet, and is a recommended step to improve your Internet experience.
The latest versions of Android browsers offer the option to activate DNS-over-HTTPS. This allows you to protect your privacy and security by redirecting DNS requests over an encrypted connection. Here are step-by-step instructions on how to activate DNS-over-HTTPS in various Android browsers:
Read Also: Quick and Easy Steps to Fix No SIM Card Error on Your Nokia 8: SIM Card Not Detected
8. Open the Mozilla Firefox browser on your Android device. 9. In the address bar, type “about:config” and press Enter. 10. Click “I accept the risk!” to continue. 11. In the search box, type “network.trr.mode”. 12. In the search result, find the “network.trr.mode” parameter and set it to “2” (enable DNS-over-HTTPS only). 13. In the search box, type “network.trr.uri”. 14. Set “network.trr.uri” to “https://dns.adguard.com/dns-query" or other desired DNS-over-HTTPS address. 15. Reload the Firefox browser for the changes to take effect. 16. Microsoft Edge:
Read Also: YouTube Error 410 Quick and Easy Fix - Troubleshooting Guide | Website Name17. Open the Microsoft Edge browser on your Android device. 18. In the address bar, type “edge://flags” and press Enter. 19. In the search box, type “DNS over HTTPS” or “Secure DNS”. 20. In the search result, find the “Secure DNS lookups” or “DNS over HTTPS” option and select “Enabled”. 21. Reload the Edge browser for the changes to take effect. 22. Opera: 23. Open the Opera browser on your Android device. 24. In the address bar, type “opera://flags” and press Enter. 25. In the search box, type “DNS over HTTPS”. 26. In the search result, look for the “DNS over HTTPS” option and select “Enabled”. 27. Reload your Opera browser for the changes to take effect.
Congratulations!!! Your Android browser now uses DNS-over-HTTPS to protect your privacy and security.
Google Chrome is one of the most popular internet browsers that allows you to activate DNS-over-HTTPS to increase security and privacy during a user session. To activate DNS-over-HTTPS in Google Chrome, you need to follow a few simple steps.
1- Open Google Chrome and type “chrome://flags” in the address bar to open the experimental feature settings. 2. Press “Ctrl + F” key to open the web page search. 3. In the search box, type “dns-over-https” and press the “Enter” key. The options to configure DNS-over-HTTPS will appear. 4. Locate the “Secure DNS lookups” option and select “Enabled” from the drop-down menu. 5. Click the “Relaunch” button to restart the browser and apply the changes.
Once restarted, Google Chrome will activate DNS-over-HTTPS, which will encrypt your DNS queries and provide more security and privacy while using the browser.
You can also check if DNS-over-HTTPS is working in Google Chrome by using special online services and tools to check the security of your DNS connection.
| Pros of DNS-over-HTTPS in Google Chrome | Cons of DNS-over-HTTPS in Google Chrome |
|---|---|
| * Security: protects against attackers changing DNS queries. |
You should be aware that activating the DNS-over-HTTPS feature in Google Chrome may change the current DNS configuration and affect the operation of some network applications. It is recommended that you carefully evaluate the pros and cons before activating this feature.
Google Chrome is one of the most popular browsers on Android, and activating the DNS-over-HTTPS (DoH) protocol in it will ensure protection and privacy when using DNS servers.
After enabling DNS-over-HTTPS in Google Chrome, the browser will use a secure connection when sending requests to DNS servers, which will help protect your privacy and keep your data safe while using the browser.
DNS-over-HTTPS (DoH) is a protocol that enables secure data transfer between a client device and a DNS server via HTTPS. Activating DoH can increase the security and privacy of your Internet connection by hiding DNS queries from unauthorized parties and preventing them from being blocked or modified.
To find out if your browser supports DNS-over-HTTPS, you can open the “chrome://flags” page in Google Chrome or “opera://flags” in Opera and search for DoH-related settings. If these settings are available in your browser, it means it supports DoH.
DNS-over-HTTPS (DoH) is a protocol that performs encryption and data protection when transmitting DNS queries over HTTPS. It provides privacy and security to users by hiding information about visited sites from the ISP.
To activate DNS-over-HTTPS in Google Chrome, you need to open your browser and type “chrome://flags” in the address bar. Find the “DNS-over-HTTPS” option, enable it and select “Required”. After that, restart the browser and DoH will be activated in Google Chrome.
5 Best Photo to Cartoon Drawing Conversion Filter App in 2023 If you are a fan of cartoons and want to turn your photos into fun and quirky cartoon …
Read ArticleThe last of us: part ii abandons multiplayer in favor of single-player content One of this year’s most anticipated games, The Last of Us: Part II, has …
Read Article5 Best Twitter VPN in 2023 With Twitter being one of the most popular social media platforms, it’s no wonder that many people want to access it from …
Read ArticleHow To Fix PS4 CE-34054-6 Error | NEW And Updated in 2023! If you are a gamer, you might have encountered the PS4 CE-34054-6 Error at some point. This …
Read ArticleReview of avaide mp4 converter - easy to use and high quality output Video file converters have become an integral part of life for many users who …
Read ArticleThe rainbow 6 siege money heist event is here. Rainbow Six Siege is a tactical first-person shooter developed by Ubisoft. The game offers team-based …
Read Article